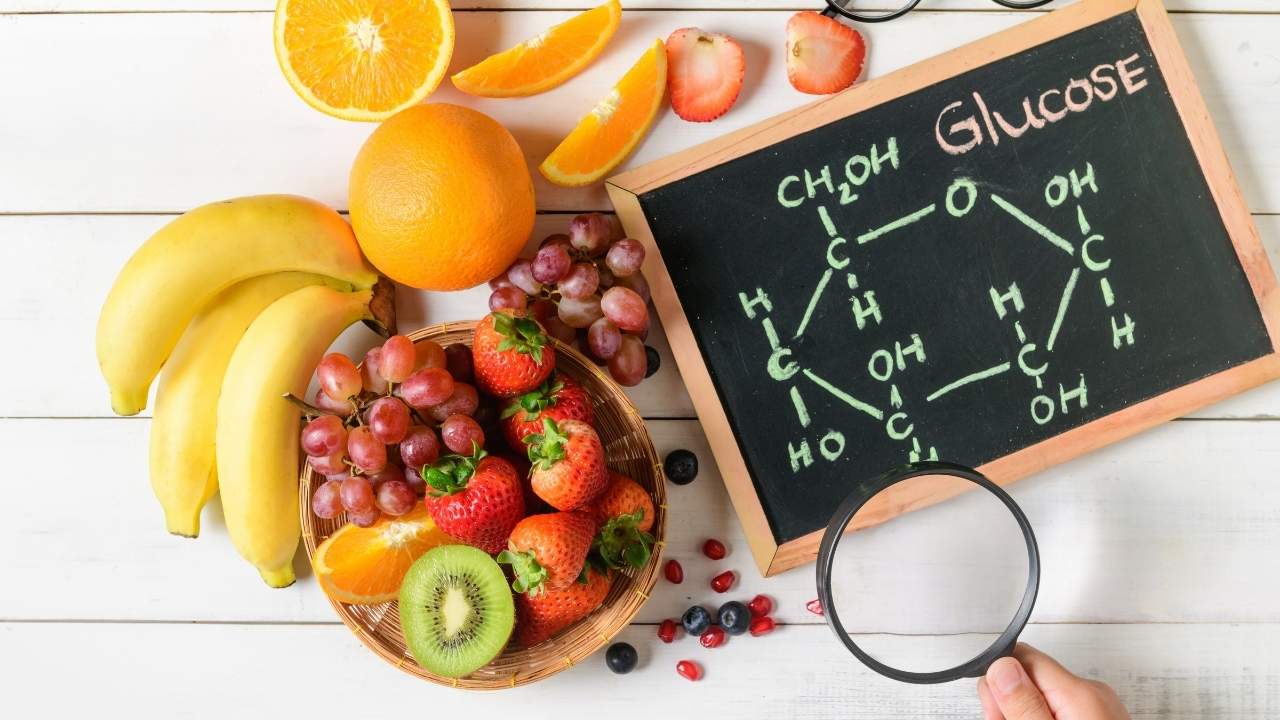Internet Asks: "Glucose Molar Mass"
Glucose, a simple sugar and a key energy source for living organisms, is an essential compound in both biochemistry and nutrition. Understanding its molar mass is crucial for various scientific and industrial applications. This article explores the molar mass of glucose and its significance in different fields.
sponsored links
What Is Glucose?
Glucose is a monosaccharide (simple sugar) with the chemical formula C₆H₁₂O₆, indicating it comprises six carbon (C) atoms, twelve hydrogen (H) atoms, and six oxygen (O) atoms. It is a primary energy source for cells and plays a significant role in metabolism. Naturally found in fruits, honey, and plant sap, glucose is also a building block for more complex carbohydrates like starch and cellulose.
Calculating the Molar Mass of Glucose
To compute the molar mass of glucose, sum the standard atomic masses of its constituent atoms:
- Carbon (C): 6 atoms × 12.01 g/mol = 72.06 g/mol
- Hydrogen (H): 12 atoms × 1.008 g/mol = 12.096 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 6 atoms × 16.00 g/mol = 96.00 g/mol
Adding these values yields:
72.06 g/mol+12.096 g/mol+96.00 g/mol=180.156 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of glucose is approximately 180.16 g/mol.
Key Facts About Glucose
- Chemical Formula: C₆H₁₂O₆
- Molar Mass: ~180.16 g/mol
- Structure: Glucose exists in both open-chain and cyclic forms, with the cyclic form predominating in aqueous solutions.
sponsored links
Significance of Glucose's Molar Mass
Understanding glucose's molar mass is crucial for:
- Biochemical Quantification: Facilitates accurate measurement of glucose concentrations in metabolic studies.
- Industrial Applications: Assists in formulating precise ingredient ratios in food and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
- Clinical Diagnostics: Enables accurate calibration of devices measuring blood glucose levels, vital for diabetes management.
Common Uses of Glucose
1. Energy Production: Glucose is metabolized in cells through glycolysis, providing energy in the form of ATP.
2. Medical Treatments: Glucose solutions are used in intravenous therapies to restore blood sugar levels.
3. Food Industry: Acts as a sweetener and energy source in various processed foods.
Fun Fact: Glucose vs. Other Sugars
Glucose is often compared to fructose and sucrose. While glucose has a molar mass of 180.156 g/mol, fructose (also C₆H₁₂O₆) shares the same molar mass but differs in structural arrangement, leading to different biological effects.
Conclusion
The molar mass of glucose, approximately 180.16 g/mol, is a fundamental property that has applications in biochemistry, medicine, food production, and chemical research. Understanding this value allows for accurate scientific measurements and practical applications across various industries.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional scientific advice.
sponsored links
References
1. Bolano, A., & Bolano, A. (2020, March 15). Molar Mass of Glucose (C6H12O6) - Science Trends. Science Trends - Explore More. https://sciencetrends.com/molar-mass-of-glucose-c%E2%82%86h%E2%82%81%E2%82%82o%E2%82%86/
2. Rana, J. (2023, May 25). Glucose (C6H12O6) molar Mass (With calculations). Knords Learning. https://knordslearning.com/glucose-c6h12o6-molar-mass/
3. Śmietańska, J. (2024, October 30). Molar Mass Calculator. https://www.omnicalculator.com/chemistry/molar-mass
People are also reading...
Why Am I Craving Sugar on Ozempic?
Sodium in Liquid IV
Sodium Correction for Glucose
Ozempic to Mounjaro Conversion Chart
How Do I Know When My Ozempic Pen Is Empty?
See the answer to: "How Do I Know When My Ozempic Pen Is Empty?"
Do You Prime Ozempic Pen Every Time?
Compound Semaglutide vs Ozempic
Can I Take Ibuprofen with Ozempic?
Coffee and Ozempic
Ready to level-up?
Create meal plans 10x faster, follow up with your clients through our mobile app, and never struggle with meal planning or recipe management again.